"Beats Flex-fragment design special edition" is now on sale on Apple's official website
11/03/2022
delivery
0コメント0件Wristband -type device with four vibration elements

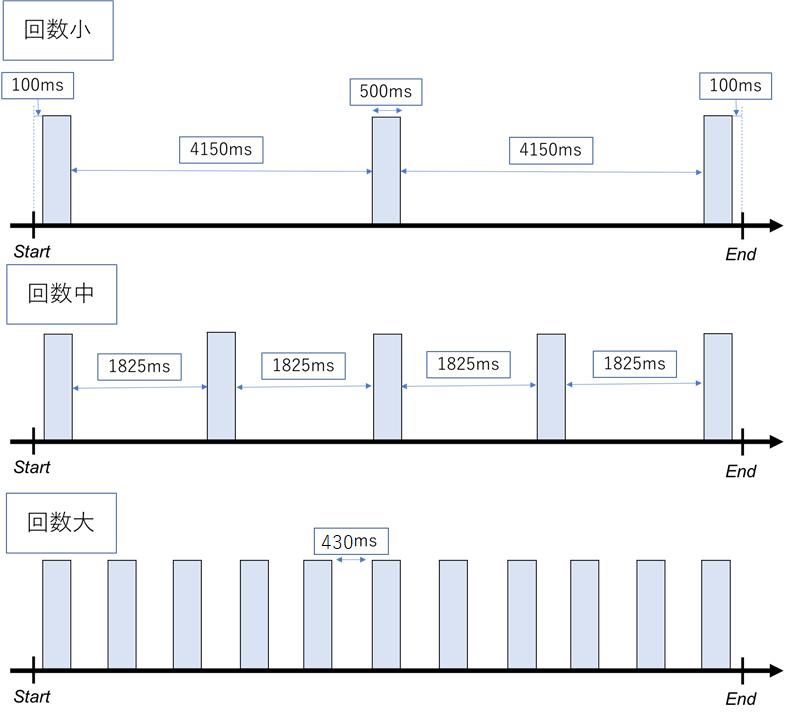
Ritsumeikan University's Murao Laboratory's research team announced by a research team "Examination of subjective time control methods using tactile stimulation / A Method To Manipulte Subjective Time by Using Tactile Stimuli of Wearable Device" (people feel subjective. This is a study that verifies whether the length of time can be operated by tactile stimulation from wrist -type devices such as smartwatches. [Image] There is a psychological phenomenon in which the subjective time of a person changes depending on the stimulus received from the outside stimulus pattern with different frequency of stimuli. Using this psychological phenomenon, we focused on wrist devices that can always be installed so that you can run subjective time anytime, anywhere. The method of presentation was a tactile sensation, not the visual or hearing of many existing methods. The tactile irritation is given vibration from the wrist to the skin. The prototype consists of four vibration elements for tactile stimulation, wristbands for attaching vibration elements, microcomputer boards (Arduino), laptops, and software for presenting stimuli. In the experiment, it was evaluated how the subjective time changes by operating the tactile stimulation pattern. Subjects evaluated the changes in subjective time in 10 seconds for 30 people in their early 20s. For tactile stimulation, three types of stimuli patterns of 10 seconds are prepared. The first event is a stimulus pattern with a different number of stimuli. Specifically, the number of stimuli is performed three times, 5 times, and 11 times. The second event is a stimulus pattern with a different duration of the stimulus. The duration of the stimulus is 5 times of 200 ms, 500ms, 5 times, and 1000ms 5 times. The third event is a stimulus pattern with a different stimulus time interval. It is performed in 5 times when the time interval of stimulus expands, 5 times at equal intervals, and narrowed. In the procedure, execute two tactile stimuli patterns and have them choose which one feels longer. The subjects experienced two types of stimuli, answered that the former was longer, the latter was longer, or both were the same. The trial was performed for three pairs with two patterns from three types of stimuli patterns. As a result of the experiment, increasing the number of stimuli increased the subjective time, reducing it as it was reduced. The result was the opposite of the pre -research conducted by hearing stimuli, and the same trend as the pre -stimulation conducted by visual stimulation. The longer the duration of the stimulus, the longer the subjective time, and the smaller it was. Even if the stimulus time was changed, the subjective time did not change in a certain trend. In the next experiment, he evaluated how the tactile stimulation can change the subjective time over the actual time. Subjects had 3 times the stimulus, 11 times, 200 ms and 1000ms of the stimulus, and the time interval of stimuli, and narrowed the time interval for 10 seconds, and how many seconds they felt. I got an answer. As a result, three stimuli the subjective time was 9.63 seconds, 3.7 % shorter than the actual time. On the other hand, 11 stimuli had a subjective time of 16.7 seconds, 16.7 % longer than the actual time. The subjective time has changed as shown in the table for other stimuli. From this result, it was found that the tactile stimulation of the wrist could be felt shorter or long than the actual time for the subject. The results can be applied not only to smart watches, but also for wearable devices such as HMD and earphones, and mobile devices such as smartphones. Utilization methods will be a wide range of ways, such as shortening the painful time to feel painful and longing exercise breaks. Source and image credits: Nozomi Shirai, Soukyo, Kazuya Murao. "Examination of subjective time control methods using tactile stimulation. ://id.nii.ac.jp/1001/00211341/Kiichi Shirai, Kyosuke Futami, and Kazuya Murao. 2021. A Method to Manipulate Subjective Time by using Tactile Stimuli of Wearable Device. In 2021 International Symposium on Wearable Computers (ISWC '21). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 63-67. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1145/3460421.3480932 Hiroki wrote. Mr. Yamashita picks up and explains a highly new nature paper.
ITMEDIA NEWS
最終更新:ITMEDIA NEWS